
After additional RNP rearrangements, the C complex catalyses the second step, resulting in the ligation of the 5' and 3' exons and release of the intron in the form of a lariat.ĭuring spliceosome assembly and catalytic activation, the snRNA components of the snRNPs, together with the pre-mRNA, form a highly complex, dynamic RNA-RNA network ( Staley and Guthrie, 1998). The B* complex catalyses the first step of splicing, generating the cleaved 5' exon and intron-3' exon lariat intermediates, and at this stage the spliceosomal C complex is generated.
The latter is converted into a catalytically active spliceosome (designated B*) by the action of the RNA helicase Prp2 ( Kim and Lin, 1996). Subsequently, association of the U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP generates the B complex that remains catalytically inactive until it undergoes extensive compositional and conformational rearrangements, including the dissociation of U1 and U4, resulting in the formation of the B act complex.

Initially, the U1 snRNP binds to the 5’ splice site (SS) and the U2 snRNP interacts stably with the branch site (BS) of the pre-mRNA, forming the A complex. Spliceosomes assemble de novo on the pre-mRNA substrate in a stepwise manner by the sequential recruitment of five small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs) and numerous non-snRNP factors (reviewed by Will and Lührmann, 2006 Wahl et al., 2009). The precise excision of an intron from a pre-mRNA and the concomitant ligation of its flanking exons (pre-mRNA splicing) are catalysed by the spliceosome, a highly dynamic ribonucleoprotein (RNP) macromolecular complex. Taken together, our data provide new insights into the RNP rearrangements and extensive exchange of proteins that occurs during spliceosome activation. The U2/U6 RNA network in B 028 complexes differs from that of the B act complex, consistent with the idea that the catalytic RNA core forms stepwise during the B to B act transition and is likely stabilized by the Prp19/CDC5L complex and related proteins. Characterization of the stalled complexes (designated B 028) revealed that U4/U6 snRNP proteins are released during activation before the U6 Lsm and B-specific proteins, and before recruitment and/or stable incorporation of Prp19/CDC5L complex and other B act complex proteins. Here, we identified a small molecule that inhibits human pre-mRNA splicing at an intermediate stage during conversion of pre-catalytic spliceosomal B complexes into activated B act complexes. Small molecule inhibitors of pre-mRNA splicing are important tools for identifying new spliceosome assembly intermediates, allowing a finer dissection of spliceosome dynamics and function.


 0 kommentar(er)
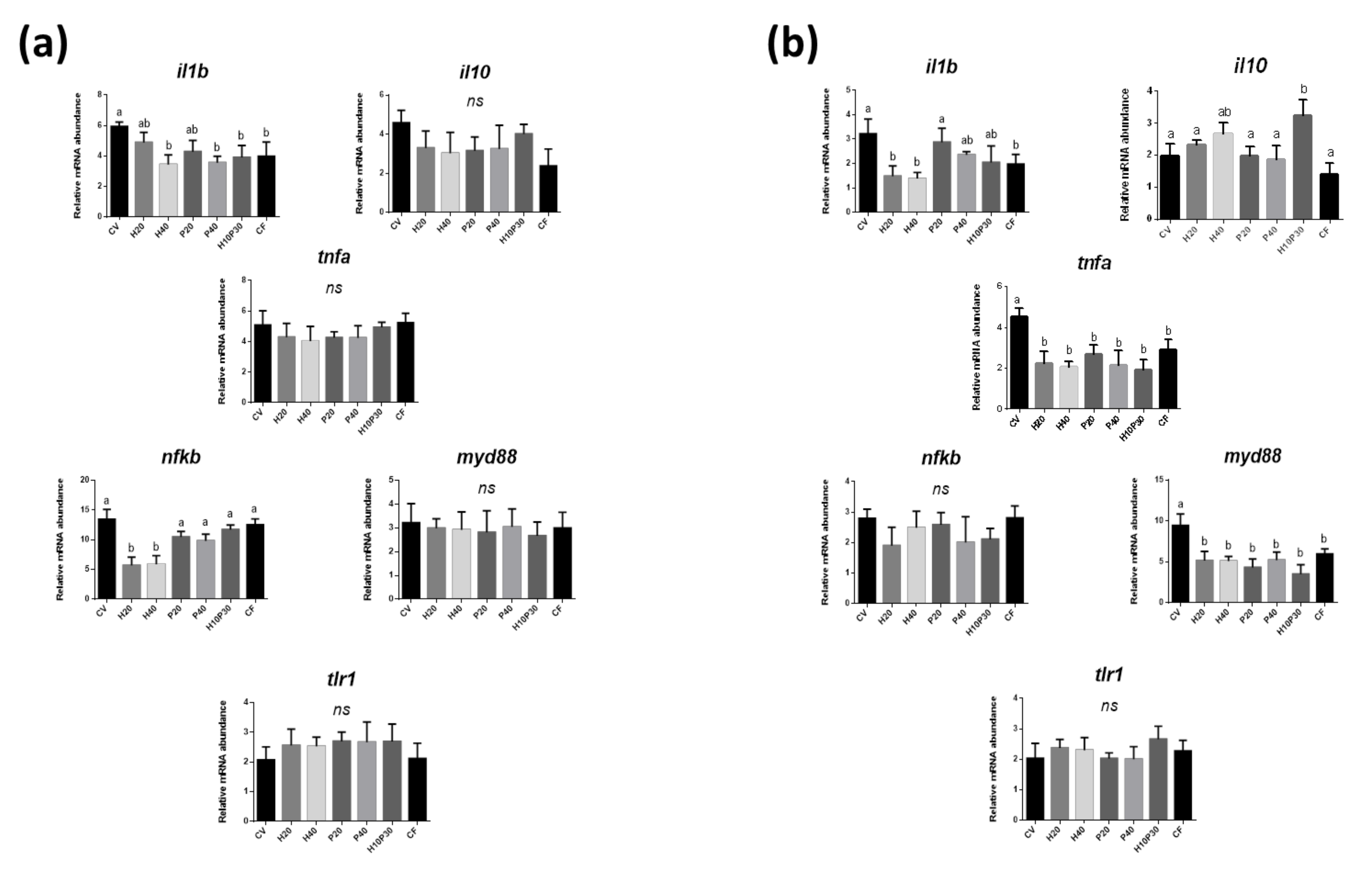
0 kommentar(er)
